Can A Fish Drown? All Of The Facts Revealed

Can fish drown? Fish are unable to breathe in the air, so how can they survive underwater without drowning? This is a question that has been debated by many.
What most people don’t know is that water actually contains oxygen which means there’s no need for fish to come up for air.
Even though this information might seem like it answers the question of can fish drown, there are still more factors involved with the process.
In order to fully understand how this works and whether or not you should be worried about your goldfish suffocating in its tank at night.
Can fish drown? Let’s take a look at what really happens.
Can A Fish Drown?
Technically, fish cannot drown because they do not have lungs like humans do. It’s more accurate to say it is a form of suffocation, and can die if they cannot pull oxygen from the water, or if the water doesn’t contain enough dissolved oxygen.
1. Damaged Gills
Damaged gills can cause fish to suffocate underwater. The gills of a fish are very important to its survival. If the gill is broken, then it won’t be able to get enough oxygen from water and this will most likely result in suffocation.
If you want your fish to live an environment where they can breathe comfortably, make sure that there’s plenty of room for them so their fins don’t touch anything or anyone else while they swim around all day!
Not only will this help keep them happy but if they’re not constantly bumping into things then their chances of getting injured decreases significantly!
2. Live Plants Taking Up Oxygen
Live plants take up oxygen inside of the aquarium, which in turn reduces the amount of oxygen that’s available for your fish to breathe.
To make sure you’re keeping up with their needs, it’s a good idea to occasionally replace live plants inside of your aquarium with fake ones!
You can also use air stones inside of your tank . These will help with the circulation of air inside of your tank, ensuring that there are always pockets for them to breathe.
3. Overcrowding
Overcrowding a fish tank can cause oxygen levels to drop, which can be detrimental for any fish inside. If you have too many fish in your tank, they’ll be fighting for oxygen and suffocate.
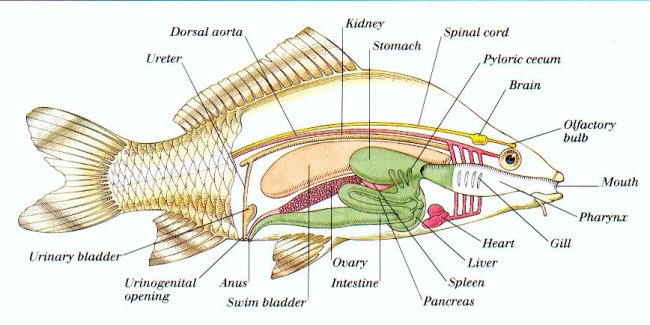
The Inner Workings Of A Fish
The liver, also known as the fish’s sludge catcher, is responsible for breaking down old blood cells and reinforcing new ones to keep oxygen pumping through the body.
The spinal cord of a fish is similar to ours. It’s a bundle of nerves that transmits all kinds of messages between the brain and body, telling it what to do.
The swim bladder is an air-filled organ fish use for buoyancy in water. Fish fill their swim bladders with oxygen at the surface then release that gas when they dive back down into deeper water so they can stay at any depth without having to expend energy on swimming up or down.”
How Do Fish Breathe And Get Oxygen?
Fish breath by using gills. These are thin, wet slits that branch off the main artery on either side of a fish’s head (the carotid), and they extract oxygen from water as it passes over them.
The gills of fish are a series of blood-filled capillaries arranged for maximal surface area to help provide them with their oxygen needs.
Oxygen is consumed through the mouth of a fish and passed to the gills. The blood in the capillaries get oxygen and is then passes it back up to the water.
Gas exchange occurs as water flowing over fish’s gills draws oxygen from the air, diffuses into a thin boundary layer of fresh water that comes into contact with each tissue.
This process is known as counter-current flow, and finally exits through openings near the base of each lamellae or filament.
Do Fish Need Oxygen
Fish, just like humans need oxygen to live. Fish have gills that extract oxygen from the water and then pass it into their blood.
Since there is more oxygen in the air than in water, living on land is much easier for humans. Fish, though, have evolved to get their oxygen from gills rather than taking it from the atmosphere like we do.
There are problems with breathing in water because the salt content of the water is higher than in air, which makes it more difficult for oxygen to dissolve into the blood.
Fish do not need a lot of oxygen because they live in water and their gills extract some from the environment around them. Salt content is another issue that can affect how much fish consume as well; if there’s too much salt in the water then less will be absorbed by their bodies.
- Saltwater fish absorb a lot of salt while respiring because it is found in the water. Consequently, they need to have some mechanism other than their kidneys to remove excess salt from their body.
- Freshwater fish have the opposite problem. There isn’t much salt in the water, so they need a mechanism to hold on to as much of it as they can.
Fish don’t need quite as much oxygen as humans do, but some fish have developed complex adaptations to maximize their oxygen uptake.
One surprising adaptation is the gas bladder which is a balloon-like organ that can be filled with air or water depending on the needs of the animal.
The swim bladders are usually used by bottom dwelling fish such as catfish and carp because they need to control buoyancy so that they don’t get stuck near the surface where there isn’t much oxygen available for them to breathe in.
The amount of oxygen inside of an aquarium depends on the volume of water inside of the tank. With a larger volume of water, there is more oxygen available to the fish than if it were in a smaller tank.
Maintaining high levels of oxygen can be difficult because even though you might have lots and lots of plants inside or outside your aquarium that are helping to increase the oxygen level, they will eventually die off so you’ll need some kind of replacement system for them in order to keep things going smoothly while also providing adequate amounts of air for your fishy friends.
Do Fish Have Lungs?
Unlike humans, fish do not have lungs, they have gills . Gills are actually very similar to the lungs in humans, but they work a little bit differently.
Gills allow water to flow across them and extract oxygen from it while also allowing carbon dioxide to escape into an organ called the “branchial sac.” This system allows fish to get their fill of oxygen without having any trouble breathing at all.
There’s a group of fish called lungfishes, which have lungs instead of gills.
They’re a small group of six freshwater species which can only be found in Australia, Africa and South America.
African and South American species can survive their habitat drying out by burrowing into the substrate and entering a state similar to hibernation. They do this by slowing their metabolism down to 1/60th of its normal rate.
How Do The Gills Of A Fish Work?
Many fish have four gills on each side of their head. The gills are made up of thin layers of tissue that contain many small blood vessels called capillaries.
The oxygen of a fish comes in through the gills on their head and face. The openings of the gills are lined with cells called epithelium, which pulls deoxygenated blood from arteries into arterioles across its surface.
Oxygen that is dissolved in water can dissolve into veins there as well before feeding to all parts of the body.
Cartilaginous fish like rays and sharks usually have five-gill slits on each side of their body. These gill slits are supported by a cartilaginous gill arch, which helps them maintain their structure. When most species of shark breathes, they need to force water over their gills, which they do by continuously swimming forward.
Saltwater fish need to expel excess sodium from their body and they do this by osmoregulation. This is the chemical process of exchanging sodium for potassium, which makes saltwater fish excrete a high concentration of water that’s flushed with excess salts and other minerals.
Can a fish survive out of water?
Fish are designed to live in water, so once they are removed from the water, they start to suffocate.
The common belief is that a fish should never be out of water for more than 10 minutes and most would not survive this length of time in dry conditions.
Certain species can die within minutes when removed from water, while others can last hours before suffocating.
Signs of Low Oxygen in Water
A common issue inside of an aquarium is low oxygen. Here are the signs to look out for:
- Rapid gill movement/labored breathing
- Lethargic
- Eating less or not at all
- Moving around less than normal
- Staying at the top (surface) of the water more than usual or for most of the day
Your fish will suffocate if you fail to resolve any of these issues.
What Causes Low Oxygen Levels in an Aquarium?
Low oxygen levels inside of an aquarium are caused by the following:
- Live plants, especially in dark tanks
- Overcrowding
- Low light levels
- Elevated water temperatures
- Certain chemicals
- Excess waste
- Algae blooms
- Decomposing plants
- Slow or zero water movement
How To Improve Oxygen Levels Inside Of An Aquarium
Here is how you can improve the levels of oxygen inside of your aquarium:
- Quantity of Fish: Work out the maximum fish per gallon you can keep for that particular species, and always aim to go lower than that number.
- Increase Aquarium Surface Area: Long shaped aquariums work better for this than tall or small aquariums.
- Increase Water Movement: The options are aquarium bubblers, spray bars, wavemakers, and powerheads.
- Correct Temperature: There is naturally more oxygen in cooler water.
Can There Be Too Much Oxygen In The Water?
Surprisingly, excess amounts of oxygen can cause your fish to die. In order for them to survive, a balance of both oxygen and hydrogen is needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
As long as the water is sufficiently oxygenated, an average fish can breathe absolutely fine at rest, as well as in motion, which means they will not drown.
Pulling a fish backwards can cause them to die because they are not able to absorb oxygen due to the water flowing in the opposite direction.
A fish may not drown in milk but it is not a good idea and can be bad for their health as they have evolved to survive in water over millions of years that contains oxygen, trace molecules, and acidity.
Conclusion
Can fish drown? Remember that fish do not have lungs and cannot drown in the same way as a human.
A fish can die if the cannot pull in enough dissolved oxygen from the water, which means they will suffocate.